- NovaScooter: Revolutionize Your Daily Commute with Smart, Sustainable Speed
- WhatsApp:+8618050955510
What is an e-scooter? When Marina, a Parisian commuter, glides through Champs-Élysées daily on her Xiaomi Pro 2, she’s participating in a transportation revolution sweeping Western cities. According to the European Transport Authority’s 2025 report, e-scooters have become the third most popular short-distance transport option in urban Europe, trailing only public transit and bicycles, with remarkable 37% market penetration. This comprehensive guide explores every aspect of these game-changing vehicles – from core mechanics to purchasing strategies, legal regulations to maintenance tips – delivering the most up-to-date and thorough e-scooter knowledge for 2025.
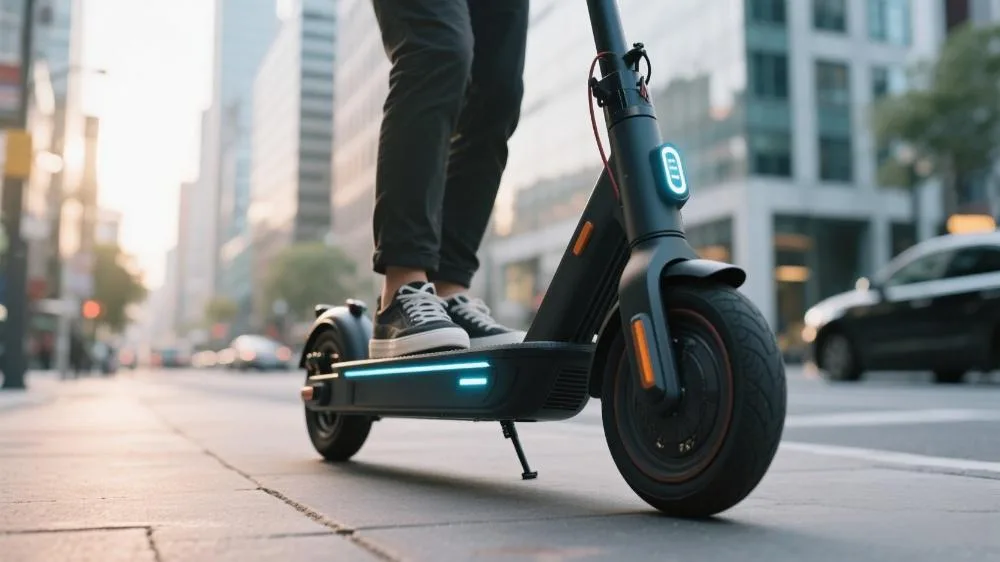

Core Components and Technical Principles
1. Power System Architecture
2025 Mainstream Configurations:
- Motor Type Comparison:
- Hub motors (82% market share): Integrated into rear wheels for easy maintenance
- Mid-drive motors (15%): Better weight distribution for performance models
- Front-wheel drive (3%): Being phased out due to safety concerns
- Battery Technology Evolution:
- Energy density: Increased from 180Wh/kg (2020) to 280Wh/kg (2025)
- Fast charging: 80% charge in 30 minutes (2025 industry standard)
- Cycle life: Premium models achieve 2,000 cycles (≥80% capacity retention)
Key Performance Metrics:
- Power rating: 350W-2,000W (EU regulated)
- Maximum torque: 15N·m to 50N·m
- Energy recovery efficiency: 25% in 2025 top models
2. Intelligent Control Systems
Five-Dimensional Control Matrix:
- Safety Features:
- Dual-brake priority circuits (EN 17128:2025 compliant)
- Automatic power reduction at ≥65°C
- Anti-skid algorithms (100x/second road analysis)
- Connectivity:
- Bluetooth 5.3 (300m range)
- 4G IoT modules (±3m positioning accuracy)
- NFC unlocking (0.3s response time)
- User Interface:
- Sunlight-readable color TFT displays (70% better visibility)
- Voice navigation (offline capability)
- Smartphone integration (e.g., novascooter recommended models)
Western Market Purchasing Guide
1. Usage Scenario Matching
Four User Profiles:
- Urban Commuters:
- Recommended range: 20-30km (accounting for winter reduction)
- Key features: Foldable design, lightweight (<15kg)
- Top pick: Segway Ninebot MAX G2
- Campus Students:
- Budget range: €400-€800
- Essentials: Anti-theft alarm, shared charging
- Popular choice: Xiaomi Essential
- Sports Enthusiasts:
- Performance needs: ≥45km/h top speed (special permit required)
- Special features: Off-road tires, adjustable suspension
- Expert recommendation: Dualtron Thunder 2
- Family Users:
- Safety focus: Speed limiter, parental controls
- Added functionality: Child seat compatibility
- Family favorite: Glion Dolly
2. Regulatory Compliance
2025 EU Regulation Highlights:
- Device Requirements:
- Mandatory front/rear lights (daytime running)
- Bell volume ≥75 decibels
- ≥20cm² reflective surfaces
- Usage Restrictions:
- 25km/h speed limit (public roads)
- Minimum age 14 (16 in some countries)
- Sidewalk riding prohibited (€100-€500 fines)
- Insurance Mandates:
- Third-party liability (minimum €1M coverage)
- Theft protection (recommended add-on)
- Personal accident (medical expense coverage)
Operation and Maintenance Masterclass
1. Daily Best Practices
Six Longevity Principles:
- Charging Habits:
- Avoid deep discharge (maintain 20%-80% charge)
- Monthly full cycle (battery calibration)
- Winter storage (keep at 50% charge, >0°C)
- Riding Techniques:
- Smooth acceleration (reduces motor stress)
- Anticipatory braking (enhances energy recovery)
- Avoid puddles (waterproof rating ≠ permanent protection)
- Regular Checks:
- Tire pressure (weekly, follow PSI markings)
- Bolt tightness (monthly torque inspection)
- Brake wear (replace pads every 500km)
2. Advanced Maintenance
DIY Toolkit Essentials:
- Must-Have Tools:
- Torque wrench (2-20N·m range)
- Digital tire gauge (±1psi accuracy)
- Waterproof grease (for charging ports)
- Troubleshooting:
- Error code interpretation (consult manuals)
- Basic circuit testing (multimeter skills)
- CAN bus diagnostics (professional tools)
- Software Management:
- Firmware updates (quarterly checks)
- System resets (fixes performance lag)
- Ride data export (usage pattern analysis)
Industry Trends and Technological Innovations
1. 2025-2030 Technology Outlook
Three Revolutionary Advances:
- Solid-State Batteries:
- 400Wh/kg energy density
- 15-minute fast charging
- Eliminated fire risks
- Smart Mobility Integration:
- V2X communication (traffic light priority)
- Auto-follow mode (safe distance maintenance)
- Congestion alerts (real-time routing)
- Material Science:
- Graphene frames (40% weight reduction)
- Self-healing tires (repairs ≤5mm punctures)
- Solar coatings (+8-10km daily range)
2. Sustainability Development
Eco-Conscious Lifecycle Management:
Certified resale market (extended product lifespan)
Manufacturing:
Carbon footprint tracking (blockchain verified)
≥30% recycled materials (2025 standard)
Renewable energy production (solar-powered plants)
Usage Phase:
Sharing economy models (300% utilization increase)
Green energy charging (certified renewables)
Zero-emission operation (full lifecycle assessment)
End-of-Life:
≥95% battery recycling (EU requirement)
Modular design (easy component replacement)
Online Message
© 2025. All Rights Reserved.